Ingredients and Their Impact
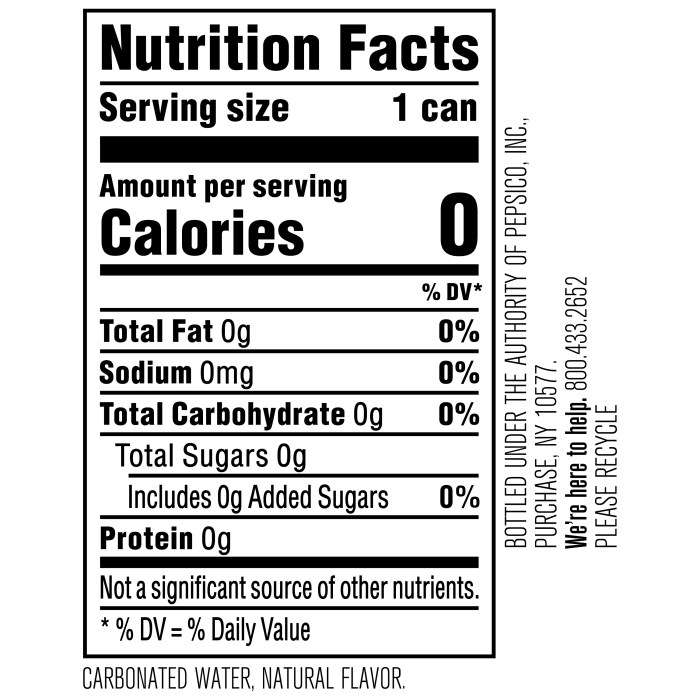
Sparkling ice nutrition facts – So, you’re curious about what makes Sparkling Ice sparkle (besides the obvious bubbles, of course)? Let’s dive into the magical world of its ingredients and see if they’re as magical as the drink itself. We’ll explore the good, the bad, and the bubbly.
Sparkling Ice’s main claim to fame is its low-calorie, low-sugar profile. This is largely achieved through the use of artificial sweeteners and a clever blend of natural flavors. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves; we need to look at the specifics.
Artificial Sweeteners
The elephant in the room (or should we say, the sugar-free elephant in the sparkling water bottle?) is the use of artificial sweeteners. Sparkling Ice typically employs sucralose and acesulfame potassium. While these provide sweetness without the caloric punch of sugar, research on their long-term health effects is ongoing and somewhat controversial. Some studies suggest potential links to gut microbiome disruption, while others find no significant negative impact.
The jury’s still out, but moderation is always a good idea, even with “zero-calorie” sweeteners. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t chug a gallon of anything, even if it was technically “healthy.”
Let’s be real, we all need to be mindful of what we consume. Understanding the sparkling ice nutrition facts is a great start to making informed choices. But to truly grasp the broader picture of fast-food nutrition, compare it to something like the detailed breakdown you can find in a McDonald’s nutrition facts pdf, available here: mcdonald’s nutrition facts pdf.
This comparison highlights the stark differences and empowers you to make healthier decisions. Remember, knowledge is power, and understanding sparkling ice nutrition facts is your first step towards a healthier lifestyle.
Natural Flavors
Ah, the mystery of “natural flavors.” This is where things get a bit vague. “Natural flavors” can encompass a wide range of ingredients derived from fruits, vegetables, or other natural sources. The exact composition isn’t always disclosed, which can be a bit frustrating for the ingredient-conscious consumer. However, the overall impression is that these flavors aim to mimic the taste of real fruit without the added sugar and calories.
It’s a balancing act between taste and transparency.
Carbonated Water
The base of Sparkling Ice is, well, carbonated water. This provides the bubbly sensation we all love and, thankfully, is pretty straightforward. Carbonated water itself doesn’t typically present significant health concerns, although excessive consumption might lead to bloating or discomfort for some individuals.
Other Ingredients and Potential Allergens
While the main components are relatively simple, it’s crucial to check the specific ingredient list for each Sparkling Ice flavor. Some flavors might contain citric acid (derived from citrus fruits), natural colors, and other additives. Always check the label for potential allergens, such as those derived from nuts or soy, which can vary by flavor. Reading the label is like a treasure hunt for the health-conscious consumer – it’s all about finding the gold (or lack of allergens) in the ingredients.
Ingredient Breakdown, Sparkling ice nutrition facts
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the typical roles played by the main ingredients:
- Carbonated Water: Provides the fizz and the base of the beverage.
- Artificial Sweeteners (Sucralose, Acesulfame Potassium): Deliver sweetness without significant calories.
- Natural Flavors: Mimic the taste of fruits or other desired flavors.
- Citric Acid (sometimes): Adds tartness and acts as a preservative.
- Natural Colors (sometimes): Enhance the visual appeal of the beverage.
Comparison with Other Beverages

Let’s face it, the beverage aisle can be a battlefield. A sugary, fizzy, artificially-sweetened free-for-all! So how does Sparkling Ice stack up against its bubbly brethren? We’re diving deep into the nutritional showdown to see who comes out on top (spoiler alert: it involves less sugar).
Sparkling Ice aims to offer a healthier alternative to traditional sodas and even some enhanced waters. This means a lower calorie count, a significant reduction in sugar, and a generally cleaner ingredient list. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves. We need to compare it to the competition to see just how much of a “healthier” choice it truly is.
Nutritional Comparison of Sparkling Ice and Competitors
To get a clearer picture, let’s compare Sparkling Ice’s nutritional profile to three common beverage types: a regular soda, a diet soda, and a naturally flavored water. Remember, nutritional information can vary depending on the specific flavor and serving size, so these are general comparisons.
| Beverage | Calories per 12 oz | Sugar (grams) per 12 oz | Artificial Sweeteners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sparkling Ice (various flavors) | 0 | 0 | No |
| Coca-Cola (Regular) | 140 | 39 | No |
| Diet Coke | 0 | 0 | Yes (Aspartame) |
| Spindrift (Naturally Flavored Sparkling Water) | 10-20 (depending on flavor) | 2-4 (depending on flavor) | No |
As you can see, Sparkling Ice shines in the “zero sugar, zero calorie” category. Regular soda is the sugary heavyweight champion, while Diet Coke uses artificial sweeteners to achieve its zero-calorie status. Naturally flavored sparkling waters like Spindrift offer a middle ground, with some calories and a small amount of natural sugar.
FAQ Summary: Sparkling Ice Nutrition Facts
Does Sparkling Ice contain caffeine?
No, Sparkling Ice does not contain caffeine.
Is Sparkling Ice suitable for people with diabetes?
While Sparkling Ice is lower in sugar than many other beverages, individuals with diabetes should still monitor their intake and consult with their healthcare provider regarding its suitability within their dietary plan.
Are there any natural flavor options available in Sparkling Ice?
Yes, Sparkling Ice offers a range of naturally flavored options, although many flavors also contain artificial sweeteners.
What are the long-term health effects of consuming artificial sweeteners?
The long-term health effects of artificial sweeteners are still being studied, and results are inconclusive. Some studies suggest potential links to various health issues, while others find no significant negative effects. Moderation is generally recommended.