Cannellini Beans and Weight Management
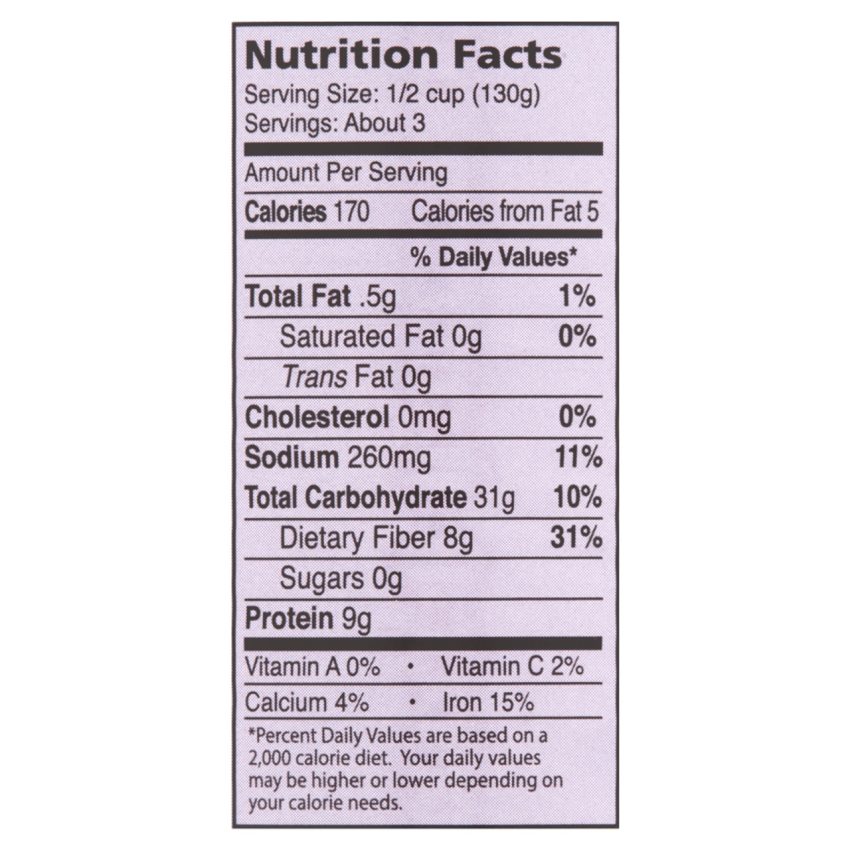
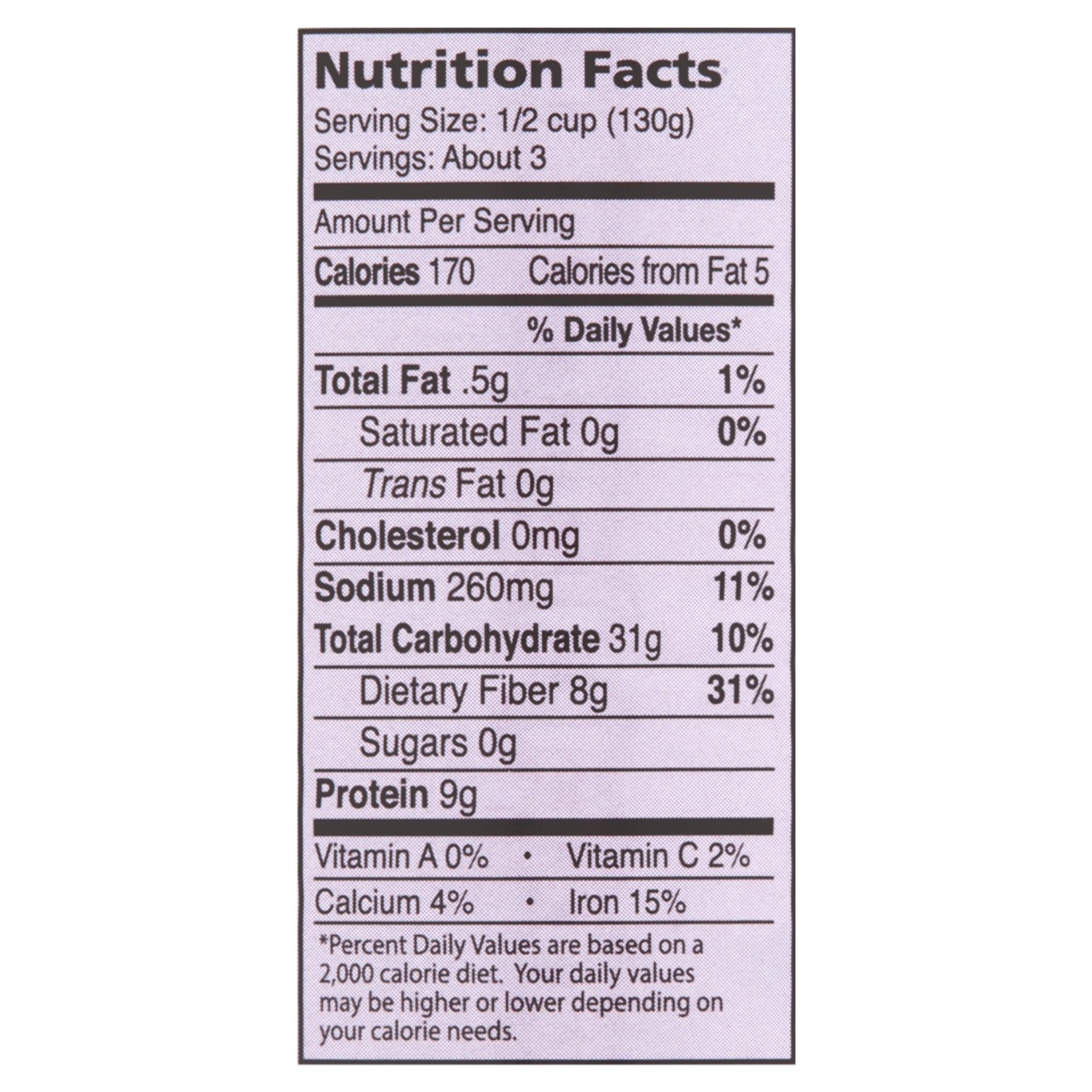
Cannellini beans nutrition facts – Embarking on a weight-loss journey can feel like navigating a complex maze, but incorporating the humble cannellini bean can be a surprisingly effective strategy. These creamy white beans are nutritional powerhouses, offering a potent combination of fiber and protein that can significantly aid in achieving your weight goals. Their unique properties contribute to feelings of fullness, helping to manage appetite and ultimately, support sustainable weight loss.Cannellini beans’ contribution to weight management stems primarily from their impressive nutritional profile.
The high fiber content sweeps through your digestive system, promoting regularity and preventing constipation. More importantly, this fiber creates a significant feeling of satiety, meaning you’ll feel fuller for longer after consuming them. This translates to reduced overall calorie intake throughout the day, a crucial factor in weight loss. Furthermore, the substantial protein content in cannellini beans helps to preserve lean muscle mass while you’re losing weight, preventing the loss of valuable tissue and boosting your metabolism.
This ensures that your body burns calories more efficiently even when at rest.
So, you’re checking out cannellini beans, huh? Those things are packed with fiber, right? But if you’re looking for something a bit more on the tart side to balance things out, check out the granny smith apple nutrition facts ; they’re surprisingly low in calories. Then you can get back to those awesome cannellini beans and their protein punch!
Glycemic Index of Cannellini Beans
Understanding the glycemic index (GI) is vital when choosing foods for weight management. The GI measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar, preventing energy crashes and promoting sustained energy levels. Cannellini beans boast a relatively low GI, making them a superior choice compared to many refined grains and other high-GI foods.
This helps to regulate blood sugar, preventing those mid-afternoon energy slumps that often lead to unhealthy snacking.
| Food | Glycemic Index | Serving Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cannellini Beans | 29 | 1/2 cup cooked | Low GI, high in fiber and protein |
| White Bread | 70 | 1 slice | High GI, refined carbohydrate |
| Brown Rice | 50 | 1/2 cup cooked | Moderate GI, whole grain |
| Kidney Beans | 29 | 1/2 cup cooked | Similar GI to cannellini beans |
Satiety and Appetite Regulation, Cannellini beans nutrition facts
The satiety effect of cannellini beans is a key factor in their ability to aid weight management. The high fiber content expands in the stomach, triggering signals to the brain that you’re full. This feeling of fullness suppresses appetite, reducing cravings and preventing overeating. Unlike many processed foods that provide a short-lived energy boost followed by a crash and subsequent hunger pangs, cannellini beans offer sustained energy and satiety, making them a valuable tool in appetite regulation.
Consider a scenario where you consume a bowl of cannellini bean soup for lunch. You’ll likely feel full and satisfied for several hours, significantly reducing the likelihood of reaching for unhealthy snacks before dinner. This sustained feeling of fullness is a crucial element in long-term weight management.
Potential Health Concerns and Interactions
While cannellini beans offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential drawbacks, especially for individuals with sensitive digestive systems or those taking specific medications. Understanding these potential concerns allows for informed consumption and helps maximize the enjoyment of these healthful legumes without experiencing unwanted side effects. Let’s explore some key areas.
Cannellini beans, like other legumes, contain complex carbohydrates and raffinose, a type of sugar that our bodies have difficulty digesting. This can lead to uncomfortable digestive issues for some people. The process of fermentation by gut bacteria, as the body tries to break down these sugars, produces gas, resulting in bloating, flatulence, and abdominal discomfort. The severity of these symptoms varies greatly from person to person, depending on individual gut microbiome composition and sensitivity.
For some, it’s a minor inconvenience, while for others, it can be quite debilitating. Starting with small portions and gradually increasing intake can help your body adjust and minimize digestive upset.
Digestive Issues Associated with High Cannellini Bean Consumption
The most commonly reported digestive issue linked to high cannellini bean consumption is gas and bloating. This is primarily due to the presence of oligosaccharides, such as raffinose, which are poorly digested in the small intestine. These undigested sugars then reach the large intestine where they are fermented by gut bacteria, producing gases like methane and carbon dioxide. This fermentation process can lead to significant abdominal discomfort, including bloating, flatulence, and cramping.
Individuals with pre-existing digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may be particularly susceptible to these effects. Soaking the beans before cooking can help to reduce the levels of these oligosaccharides, potentially mitigating the digestive issues.
Interactions with Medications
Cannellini beans, being rich in various nutrients, can potentially interact with certain medications. While research on specific interactions is limited, it’s important to be mindful of the possibility. For example, the high fiber content in cannellini beans could potentially interfere with the absorption of certain medications, reducing their effectiveness. This is especially relevant for medications that require a specific level of absorption in the gut.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist if you are taking medication and planning to significantly increase your cannellini bean intake. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific medications and health conditions.
Visual Representation of a Cannellini Bean
Imagine a small, kidney-shaped bean, roughly an inch long. Its color is a creamy, almost off-white, with a subtle, pearly sheen. The surface is smooth, with a slightly wrinkled texture, hinting at its natural form. The bean feels firm to the touch, with a dense, compact consistency before cooking, transforming into a softer, more tender texture after being cooked.
Its shape is not perfectly uniform; each bean possesses a unique, slightly irregular form, a testament to its natural origin.
FAQ: Cannellini Beans Nutrition Facts
Are canned cannellini beans as nutritious as dried?
Dried cannellini beans generally contain more fiber and fewer sodium, but canned beans offer convenience. Choose low-sodium canned varieties to minimize sodium intake.
Can I eat cannellini beans every day?
While cannellini beans are nutritious, consuming them daily might lead to digestive discomfort for some due to their high fiber content. Moderation is key.
Do cannellini beans cause gas?
Yes, like many legumes, cannellini beans can cause gas and bloating in some individuals. Soaking and properly cooking them can help reduce this effect.
How should I store cannellini beans?
Dried beans should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Canned beans should be stored in a cool, dark place after opening and used within a few days.